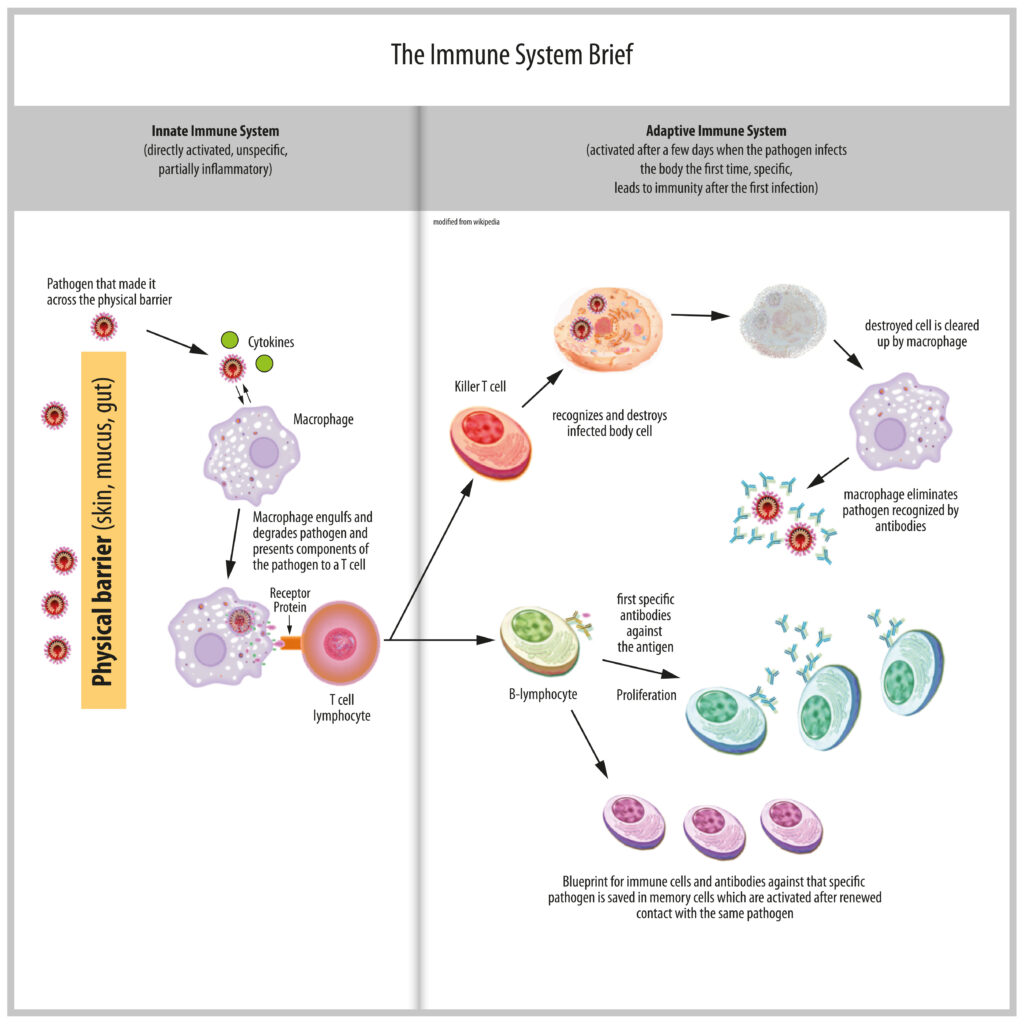
Beta glucans are naturally occurring polysaccharides which are part of the cell wall of pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Though that sounds adventurous, beta glucans are absolutely safe for consumption and have some unique immune stimulating properties. Small amounts of beta glucan as contained in our product can increase the immune defense by stimulating the function of macrophages and killer cells[1]. This is achieved by the fact that beta glucans are recognized by receptors of the immune system which then trigger an immune response. By that, a part of the immune system is constantly active ready to fight pathogens when they enter the body [2]. *
Vitamin D is the only vitamin which can be produced by the body when exposed to sun. Not surprisingly, in winter times, a vitamin D deficiency can therefore occur. This is an unfortunate combination of events, since especially during the cold season where infections appear the most, vitamin D is essential for a proper immune response. Studies show that vitamin D is important to counteract inflammatory reactions caused by macrophages which are triggered during the innate immune reaction [3]. As described in the introduction, the innate immune response is not exclusively beneficial since it triggers inflammation which can further weaken the body. During Corona pandemic vitamin D gained special interest as many studies show that it helps prevent infections of the upper respiratory tract. Though the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, there is a clear correlation between the plasma concentration of vitamin D which is especially low during winter but also in the elderly, and the risk of respiratory infections as caused by viruses such as Sars-Cov2 and influenza [4]. *
Vitamin B12 is an important vitamin for the whole energy metabolism of the body. Generally, vitamin B12 helps to fight tiredness and fatigue which often come along with infections. Recent studies could also show that the vitamin helps the specialized cells of the adaptive immune system to stay healthy and functional [9]. *
Vitamin C is potentially the vitamin with the most awareness when it comes to immune support. Although a balanced and healthy diet should ensure a sufficient intake of vitamin C, some distinct circumstances can lead to an increased need for that vitamin C. Especially during infections, the body needs more vitamin C than usual. Vitamin C acts in the innate and adaptive immune response by supporting the epithelial barrier function as the first instance against invading pathogens. Moreover, it accumulates in phagocytic cells where it can support their function in destroying pathogens. Additionally, vitamin C is a strong antioxidant which helps to fight oxidative stress caused by oxygen radicals. This stress is caused by environmental factors but is also high during infections. Vitamin C can bind these reactive oxygen molecules and avoid them to trigger inflammations and damage tissue. Studies show that supplementation with 100 mg Vitamin C a day can already suffice to reach a vitamin C level in the body that helps to prevent infections while high amounts in the range of a gram or more can significantly improve the outcome and duration of an infection [5]. *
Although zinc is only needed in low amounts, the side effects of a zinc deficiency clearly show how important this trace element is for the immune system. Low zinc levels come along with imbalanced immune reactions which can favor allergies and inflammatory diseases [6]. Similar to vitamin C, zinc is increasingly consumed by the body during infection to regulate inflammatory reactions caused by invading pathogens. A balanced zinc level helps to downregulate the harmful unspecific immune response of the innate immune system and to upregulate the specific reactions of the adaptive immune system [7]. Studies show that zinc works best in combination with vitamin C. Both nutrients together can shorten the duration of respiratory tract infection and improve the incidence of pneumonia by optimizing the interplay of the different parts of the immune system [8]. *
Blueberries are potentially the most antioxidant-rich fruits our planet has to offer. The blueberry is loaded with special polyphenols, so-called anthocyanins, which protect the body from free radicals[10]. Radicals are formed due by environmental factors but also develop during infections. Consuming blueberries or extracts thereof can help to fight oxidative stress and increase the amount of killer T cells and anti-inflammatory components [11]. *
Selenium has strong antioxidant capacities and helps to fight oxidative stress caused by infections and environmental factors. Selenium can boost the immune system by reducing the inflammatory response and increasing the number of specialized immune cells, such as T cells during viral infections [12] [13]. *
Trace elements such as zinc are particularly important for the immune system. However, these nutrients have to be transported to where they are needed. In case of an infection, they have to reach immune cells which need the nutrient to work properly. The amino acid L-histidine can bind to zinc forming a complex that allows zinc to cross the membrane of immune cells [14]. In addition to that, low levels of histidine could be shown to inhibit the immune response [15]. *
Willow bark contains an active chemical compound called salicin. Salicin is converted to salicylic acid by the human body. Hence, willow bark is also called “nature’s aspirin”. The effects of taking salicin or milder than taking aspirin, but salicin is quite stomach-friendly when taken in moderate doses. Salicin can help to fight inflammations and is used in the traditional medicine to lower fever [16].
Propolis has been scientifically shown to contain more than 300 active compounds, with polyphenols as the most abundant. These work anti-oxidative and give Propolis certain antibacterial, antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties [17], [18]
Rose hip has a remarkably high content of antioxidants, e.g. polyphenols, carotenoids as well as vitamin C and E [19]. All together, these components can help to strengthen the immune system and to protect cells from free radicals[20].
Manuka honey originates from New Zealand and has – in contrast to other honeys – some unique properties. Manuka honey has a remarkable antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect and is often used for wound healing, treatment of sore throats and for relief of the common cough [21] [22].
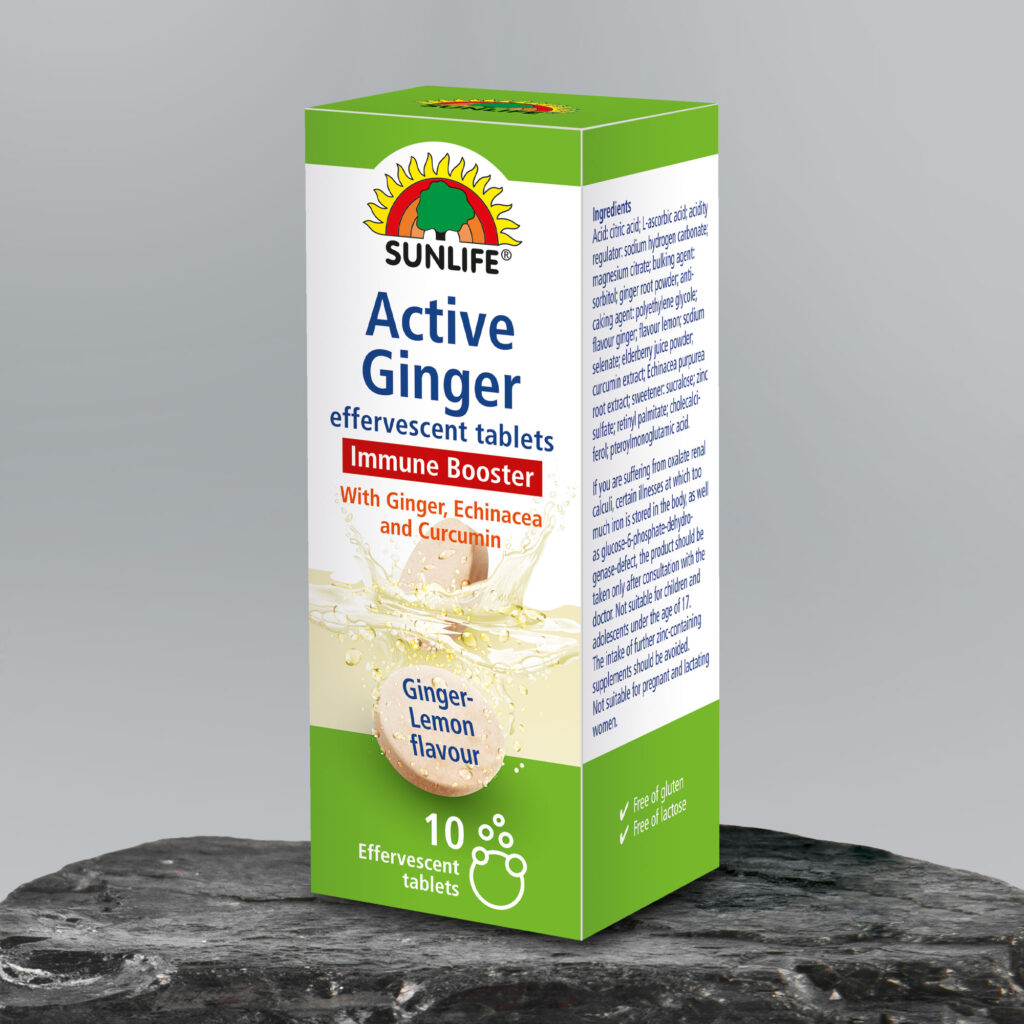
Ginger has a long history of use in traditional and alternative medicine. It has not only been used to aid digestion and reduce nausea but it also helps to fight flu and common colds. The main bioactive compound of ginger is Gingerol, which is responsible for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects [23].
Elderberries are loaded with special polyphenols, called anthocyanins, which give the fruit its characteristic dark purple color. In folk medicine, elderberry is used since centuries to treat flu and common colds. This effect, mostly achieved by the anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory power of anthocyanins and other contained bioactive compounds, has been recently also been shown by various scientific studies which report a significant reduction in infection durations [24] [25].
Echinacea purpurea contains some rare bioactive compounds called rosmarinic acid, chicoric acid and flavonoids. These anti-oxidants are paired with alkamides which further enhance the radical-fighting capacities of this plant by renewing used anti-oxidants and targeting them to cells that are especially prone to oxidative stress [26]. Proven by numerous studies, the anti-oxidative power of Echinacea effectively reduces the duration of cold symptoms and has a certain preventive effect [27].
Curcumin is the bioactive compound of turmeric, the spice that gives the yellow color to curries. Nowadays its known, that turmeric (or better its contained curcumin) can do much more than giving color to foods. In the last few years, scientific data bases are more and more packed with studies showing positive effects of curcumin on health. Besides many benefits, the most important function of curcumin in immunity, is to block the transport of a certain molecule, that triggers strong inflammations in the cell. This molecule is also involved when pathogens enter the body and leads to symptoms like fatigue and fever which can further weaken the body [28] [29].
Magnesium is involved in both, the unspecific and specific immune response. It has various functions in the ability of immune cells to bind invading pathogens and helps the antibody-dependent destruction of infected cells. Magnesium imbalances especially occur in the elderly, where it leads to defective membrane functions, inflammations and immune dysfunction making this mineral particularly important for the older generation [32].
Vitamin A is important to maintain the structure of cells in skin, respiratory tract and gut. These structures form the first physical barrier against evading pathogens. Therefore, vitamin A can be seen as a gatekeeper for the immune system. Vitamin A is also required for the production of antibodies which neutralize harmful viruses or bacteria that enter the body and supports the cell differentiation into T cells [30].
Folic acid is basically needed for every mechanism in the body that involves cell divison and proliferation. Since specialized immune cells have to be formed upon infection, this vitamin is particularly important for the immune response. [31]
* These are summaries of scientific data of the indicated original publications. None of these statements has been evaluated by the EFSA. Food supplements are not intended to treat or cure any disease. Food supplements are not a substitute for a balanced diet and a healthy way of living.